Aktuelles aus der Forschung
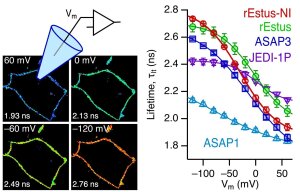
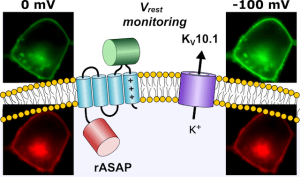
Membrane voltage measured with FLIM
Abbildung: FSU BiophysikFluorescence lifetime imaging of membrane voltage
Nair, A.G., M. Rodewald, H. Bae, P. Rühl, J. Popp, M. Schmitt, T. Meyer-Zedler, S.H. Heinemann
Absolute membrane potential recording with ASAP-type genetically encoded voltage indicators using fluorescence lifetime imaging
ACS Chemical Neuroscience (2025) 10.1021/acschemneuro.5c00670. PMID: 41273308
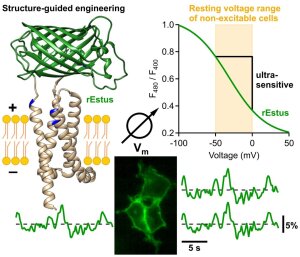
rEstus, a fluorescent membrane voltage indicator
Abbildung: FSU BiophysikVisualizing the electrical whispering of cells
Rühl, P., A.G. Nair, N. Gawande, S.N.C.W. Dehiwalage, L. Münster, R. Schönherr, S.H. Heinemann
An ultrasensitive fluorescent voltage indicator unvovers the electrical acivity of non-excitable cells
Advanced Science (2024) e2307938. PMID: 38526185
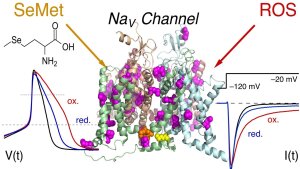
SeMet-containing sodium channels
Illustration: FSU BiophysikSeMet-containing sodium channels
Hussein, R.A., M. Ahmed, S.H. Heinemann
Selenomethionine mis-incorporation and redox-dependent voltage-gated sodium channel gain of function
Journal of Neurochemistry (2023) 167(2): 262-276. PMID: 36152916
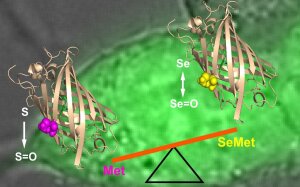
SeMet Incorporation
Illustration: FSU BiophysikOptical sensing of SeMet incorporation
Hussein, R.A., M. Ahmed, N. Kuldyushev, R. Schönherr, S.H. Heinemann
Selenomethionine incorporation in proteins of individual mammalian cells detected with a genetically encoded fluorescent sensor
Free Radical Biology and Medicine (2022) 192: 191-199. PMID: 36152916
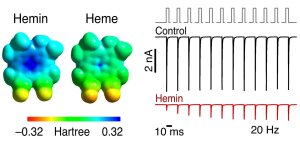
Hemin inhibits cadiac NaV channels
Abbildung: FSU BiophysikExtracellular hemin inhibits cardiac voltage-gated Na+ channels
Gessner, G., M. Jamili, P. Tomczyk, D. Menche, R. Schönherr, T. Hoshi, S.H. Heinemann
Hemin is a reverse use-dependent gating modifier of cardiac voltage-gated Na+ channels
Biological Chemistry (2022) 403: 1067-1081. PMID: 36038266
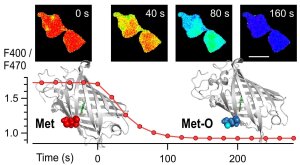
Fluorescent Sensor for Methionine Oxidation
Illustration: FSU BiophysikOptical monitoring of protein posttranslational modification
Kuldyushev, N., R. Schönherr, I. Coburger, M. Ahmed, R.A. Hussein, E. Wiesel, A. Godbole, T. Pfirrmann, T. Hoshi, S.H. Heinemann
A GFP-based ratiometric sensor for cellular methionine oxidation
Talanta (2022) 243:123332. PMID: 35276500
Genetically Encoded Voltage Indicator
Illustration: FSU BiophysikOptical tracking of membrane potential in cell cultures
Rühl, P., J. Langner, J. Reidel, T. Hoshi, R. Schönherr, S.H. Heinemann
Monitoring of compound resting membrane potential of cell cultures with ratiometric genetically encoded voltage indicators
Communications Biology (2021) 4:1164. PMID: 34620975
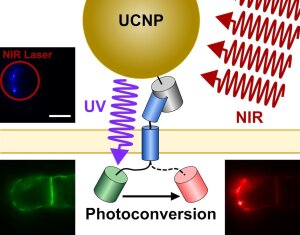
Photoactivation of Dendra2 by NIR radiation of UCNPs
Illustration: FSU BiophysikPhotonic modulation with upconverting nanoparticles
Drees, C., P. Rühl, J. Czerny, G. Chandra, J. Bajorath, M. Haase, S.H. Heinemann, J. Piehler
Diffraction-unlimited photomanipulation at the plasma membrane via specifically targeted upconversion nanoparticles
Nano Letters (2021) 21:8025-8034. PMID: 34519216
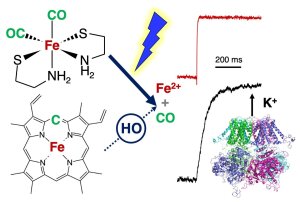
CORM-S1 releases CO and Fe2+, both of which activate BK channels
Illustration: FSU BiophysikRapidly photoreleased Fe2+ activates BKCa channels
Gessner, G., P. Rühl, M. Westerhausen, T. Hoshi, S.H. Heinemann
Fe2+-mediated activation of BKCa channels by rapid photolysis of CORM-S1 releasing CO and Fe2+
ACS - Chemical Biology (2020) 15(8): 2098–2106. PMID: 32667185
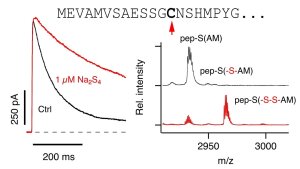
N-terminal sequence of Kv1.4 (top); current traces of Kv1.4 before and after polysulfide application (left); MALDI spectra showing sulfhydration of C13 in the N-terminal inactivation peptide.
Illustration: FSU BiophysikSulfhydration eliminates potassium channel inactivation
Yang, K., I. Coburger, J.M. Langner, N. Peter, T. Hoshi, R. Schönherr, S.H. Heinemann
Modulation of K+ channel N-type inactivation by sulfhydration through hydrogen sulfide and polysulfides
Pflügers Archiv European Journal of Physiology (2019) 471: 557-571. PMID: 32388729
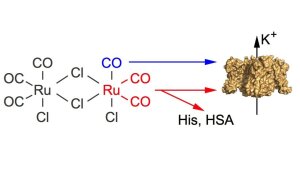
Dual effects of tricarbonyldichlororuthenium(II) dimer (CORM-2) on voltage-dependent potassium channels. Channel modification may result from binding of either carbon monoxide (blue) and/or of Ru(CO)2 fragments (red). The latter involves adduction to target histidines and, thus, can be quenched by excess free histidine or histidine-containing proteins such as human serum albumin.
Illustration: FSU BiophysikCO-releasing molecules standing offside?
Gessner, G., N. Sahoo, S.M. Swain, G. Hirth, R. Schönherr, R. Mede, M. Westerhausen, H.H. Brewitz, P. Heimer, D. Imhof, T. Hoshi, S.H. Heinemann
CO-independent modification of K+ channels by tricarbonyldichloro-ruthenium(II) dimer (CORM-2).
European Journal of Pharmacology (2017) 815: 33-41
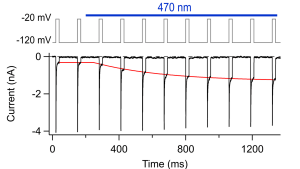
Pulse protocol (top) and current recordings of roNaV2 channels in HEK293 cells (bottom). The blue bar marks illumination of the cell with blue light via a 63x objective. The red curve is a mono-exponential fit to describe the time course of inactivation loss upon illumination.
Illustration: FSU BiophysikSodium channel with selenocysteine senses phototoxicity
Ojha, N.K., E. Leipold, R. Schönherr, T. Hoshi, S.H. Heinemann
Non-photonic sensing of membrane-delimited reactive species with a Na+ channel protein containing selenocysteine.
Scientific Reports (2017) 7: 46003
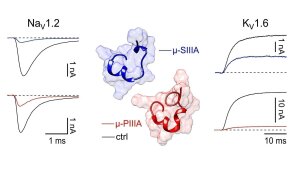
Blocking effects of 10 µM µ-SIIIA (blue) and µ-PIIIA (red) on ion currents of the indicated voltage-gated ion channels.
Illustration: FSU Biophysikµ-Conotoxins block Kv channels
Leipold, E., F. Ullrich, M. Thiele, A.A. Tietze, H. Terlau, D. Imhof, S.H. Heinemann
Subtype-specific block of voltage-gated K+ channels by µ-conotoxins.
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications (2017) 482: 1135-1140
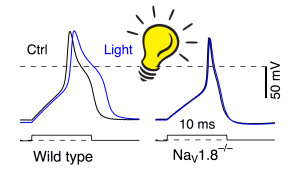
Stimulated action potentials of DRG neurons before (black) and after 150 s illumination with blue light (blue) from wild-type (left) and NaV1.8-deficient mice (right).
Illustration: FSU BiophysikStress susceptibility of Nav1.8 channels in DRG neurons
Schink, M., E. Leipold, J. Schirmeyer, R. Schönherr, T. Hoshi, S.H. Heinemann
Reactive species modify Nav1.8 channels and affect action potentials in murine dorsal root ganglion neurons
Pflügers Archiv European Journal of Physiology (2016) 468: 99-110
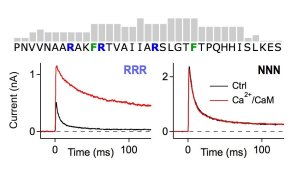
Score pattern for potential calmodulin binding to the N terminus of Kvβ1.1 (top) and current recordings of Kv1.1+Kvβ1.1 channels with and without Ca(2+)/CaM for wild-type Kvβ1.1 (left) and after replacement of three asparagine residues for arginine (right).
Illustration: FSU BiophysikFine-tuning of Kv channel inactivation by calcium
Swain, S.M., N. Sahoo, S. Dennhardt, R. Schönherr, S.H. Heinemann
Ca/calmodulin regulates Kvβ1.1-mediated inactivation of voltage-gated K+ channels.
Scientific Reports (2015) 5: 15509
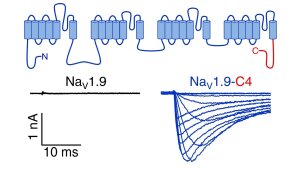
Representative current traces measured in the whole-cell mode in response to depolarizations ranging from -127 to 3 mV of HEK 293T cells expressing human NaV1.9 (left) or chimera NaV1.9-C4 (right).
Illustration: FSU BiophysikFunctional expression of Nav1.9 chimeras
Goral, R.O., E. Leipold, E. Nematian-Ardestani, S.H. Heinemann
Heterologous expression of Nav1.9 chimeras in various cell systems.
Pflügers Archiv European Journal of Physiology (2015) 467: 2423-2435
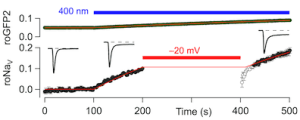
Response of roGFP2 (top) and the ratiometric roNaV signal (bottom) to blue light. At -50 mV roNaV is inactivated and, thus, protected from ROS attack.
Illustration: FSU BiophysikroNaV: A non-photonic gateable ROS sensor
Ojha, N.K., E. Nematian-Ardestani, S. Neugebauer, B. Borowski, A. El-Hussein, T. Hoshi, E. Leipold, S.H. Heinemann
Sodium channels as gateable non-photonic sensors for membrane-delimited reactive species.
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta - Biomembranes (2014) 1838: 1412-1419
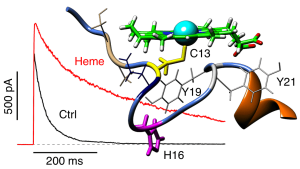
Kv1 4 current traces without (black) and with hemin (red). Part of the N-terminal ball domain with a docked hemin moiety.
Illustration: FSU BiophysikHeme is a potent regulator of potassium channel inactivation
Sahoo, N., N. Goradia, O. Ohlenschläger, R. Schönherr, M. Friedrich, W. Plass, R. Kappl, T. Hoshi, S.H. Heinemann
Heme impairs the ball-and-chain inactivation of potassium channels.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA Plus (2013) 110: E4036-4044
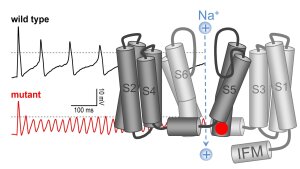
A mutation in SCN11A causes a gain-of-function of the voltage-gated sodium channel NaV1.9 and leads to suppression of the electrical signaling in nociceptive neurons.
Illustration: FSU BiophysikA mutation in SCN11A eliminates pain sensation
Leipold, E., L. Liebmann, G.C. Korenke, T. Heinrich, S. Gießelmann, J. Baets, M. Ebbinghaus, R.O. Goral, T. Stödberg, J.C. Hennings, M. Bergmann, J. Altmüller, H. Thiele, A. Wetzel, P. Nürnberg, V. Timmerman, P. de Jonghe, R. Blum, H.G. Schaible, J. Weis, S.H. Heinemann, C.A. Hübner, I. Kurth
A de novo gain-of-function mutation in SCN11A causes loss of pain perception.
Nature Genetics (2013) 45: 1399-1404
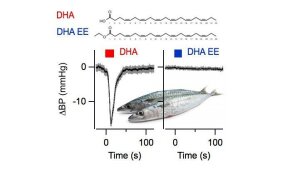
Blood pressure recordings on anesthesized mice upon injection of DHA and DHA EE (experiments performed by Bianka Wissuwa).
Illustration: FSU BiophysikOmega-3 fatty acids lower blood pressure
Hoshi, T., B. Wissuwa, Y. Tian, N. Tajima, R. Xu, M. Bauer, S.H. Heinemann, S. Hou
Omega-3 fatty acids lower blood pressure by directly activating large-conductance Ca2+-dependent K+ channels
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA (2013) 110: 4816-4821