Optical sensing of selenomethionine incorporation
SeMet Incorporation
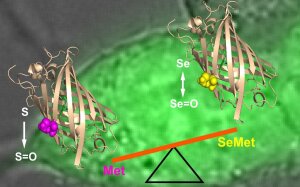
Illustration: FSU BiophysikSelenomethionine (SeMet) randomly replaces methionine (Met) in protein translation. Because of strongly differing redox properties of SeMet and Met, SeMet mis-incorporation may have detrimental effects on protein function, possibly compromising the use of nutritional SeMet supplementation as an anti-oxidant. Studying the functional impact of SeMet in proteins on a cellular level is hampered by the lack of accurate and efficient methods for estimating the SeMet incorporation level in individual viable cells. Here we introduce and apply a method to measure the extent of SeMet incorporation in cellular proteins by utilizing a genetically encoded fluorescent methionine oxidation probe. Kinetics and extent of SeMet incorporation on the single-cell level under live-cell imaging conditions provided direct access to protein turn-over kinetics and SeMet redox properties in a cellular context.